Feb 13, 2025
Sealing joints in pipes and fittings is inseparable from sealing rings. Among common pipe threads, the G thread is a cylindrical thread and does not have self-sealing properties.
While PT and NPT threads are tapered threads and have certain self-sealing characteristics, in practical applications, the sealing of threaded connections is often not guaranteed due to the impact of thread processing accuracy. Therefore, additional sealing measures are still required to seal the pipe joints.
Sealing rings are one of the widely used additional sealing measures. In the market, NBR and EPDM are the most common sealing ring materials, with EPDM seals also being widely applied. Due to differences in chemical composition, performance characteristics, and suitable applications, each has its advantages in specific uses.

NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber) is a synthetic rubber made by polymerizing butadiene and acrylonitrile. It has strong oil resistance, making it widely used in sealing applications where oil leakage needs to be prevented. Its molecular structure gives it good resistance to petroleum-based products such as lubricating oils, gasoline, and diesel.
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) is a synthetic rubber made by polymerizing ethylene, propylene, and a small amount of diene monomer. Compared to NBR, the molecular structure of EPDM gives it excellent weather resistance, UV resistance, and ozone resistance, making it more durable when exposed to natural environments.
NBR: The most notable characteristic of NBR seals is their strong oil resistance. They maintain good sealing performance when in contact with oils, fuels, solvents, and other chemicals, and are widely used in automotive, industrial hydraulic systems, and oil and gas pipelines. In addition, NBR has some corrosion resistance to weak acids and bases, but its resistance to strong acids, strong bases, and oxidizers is weaker.
EPDM: EPDM seals have excellent resistance to acids, bases, water, and steam, making them highly suitable for environments where they come into contact with water, steam, or chemicals (e.g., detergents). However, their resistance to most oils and fuels is poor.
NBR: NBR seals typically have a temperature range of -30°C to 100°C, with special formulations able to withstand higher temperatures. However, compared to EPDM, its high-temperature resistance is slightly inferior. NBR also performs poorly in low temperatures and may become brittle in extreme cold.
EPDM: EPDM seals have a broader temperature range, generally usable from -40°C to 150°C, offering stronger high-temperature and low-temperature performance. They are particularly suitable for environments with significant temperature fluctuations, such as high-temperature steam and hot water pipeline systems.
NBR: While NBR has good wear resistance and a relatively long service life, its weather and UV resistance are poor. Prolonged exposure to sunlight, especially ultraviolet rays, can cause NBR to age and harden, leading to seal failure.
EPDM: EPDM performs better in this regard. It has excellent resistance to UV rays, ozone, and aging, allowing it to be exposed to outdoor environments for long periods without degradation. Therefore, it is widely used in sealing applications exposed to the atmosphere for extended periods, such as automotive window seals and building window seals.
NBR: NBR has high mechanical strength, excellent elasticity, and tensile properties, making it suitable for sealing applications under high pressure, rapid movement, or heavy loads. It also has good wear resistance and can effectively resist damage caused by friction.
EPDM: Although EPDM excels in temperature and aging resistance, its elasticity and compression resistance are slightly inferior to NBR. It is more suitable for applications requiring resistance to weather changes, water, or steam, and its performance under high mechanical pressure is somewhat limited.
NBR: Due to its excellent oil resistance and wear resistance, NBR seals are typically used in automotive seals, oil seals, hydraulic systems, fuel pipelines, and mechanical equipment. NBR is ideal for any application that involves sealing oils, fuels, and hydraulic oils.
EPDM: EPDM seals are widely used in the construction, automotive, and household appliance industries, particularly in environments requiring high-temperature, water, UV, and steam resistance. EPDM is commonly used in automotive cooling systems, window seals, washing machines, and water heaters.
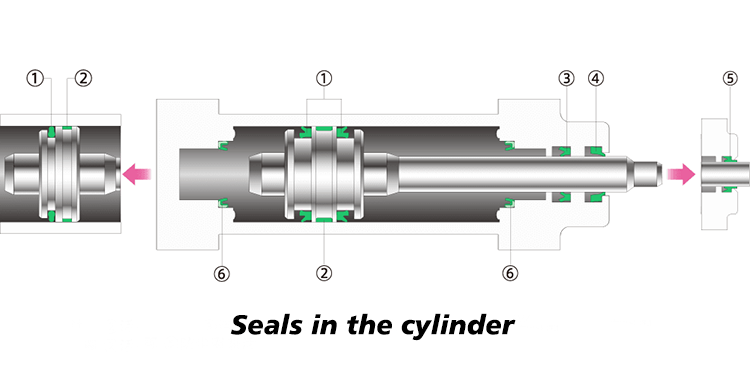
Typically, NBR seals are less expensive, making them a cost-effective choice for many standard industrial applications. In contrast, EPDM seals are slightly more expensive, but their excellent weather and high-temperature resistance make them a more cost-effective choice for long-term, high-performance sealing applications.
Item | NBR Material Seal | EPDM Material Seal |
Material Properties | Synthetic rubber made from butadiene and acrylonitrile | Synthetic rubber made from ethylene, propylene, and non-conjugated diene monomers |
Hardness | Shore A hardness 60-80 | Shore A hardness 70-90 |
Wear Resistance |
Average, but performs better in oily and lubricated environments
| Good, especially under high-temperature conditions |
Aging Resistance | Ages quickly under sunlight and air exposure, slowed in oily environments | Strong aging resistance under sunlight, air, and high-temperature conditions |
Weather Resistance | Poor, prone to aging outdoors | Excellent, resists UV rays, ozone, and extreme weather |
Oil Resistance |
Excellent
| Poor |
Chemical Corrosion Resistance | Average | Excellent, resists acids, bases, steam, etc. |
Working Temperature Range | -30°C to 100°C | Typically -40°C to 125°C, special formulations can reach 150°C |
Application Fields | Oil seals, O-rings, sealing rings, fuel pipelines, hydraulic systems, etc. | Automotive cooling systems, construction sealing materials, electrical insulation, etc. |
NBR seals primarily offer excellent oil and wear resistance, are cost-effective, and are suitable for environments that require resistance to oils, fuels, and hydraulic systems. In contrast, EPDM seals are characterized by high-temperature, UV, acid, base, and steam resistance, with a higher price, typically used in specific high-performance applications.
You May Interest In
FOKCA ©1998-2025 All Rights Reserved Sitemap